The spinal cord is divided into
four main regions:
-
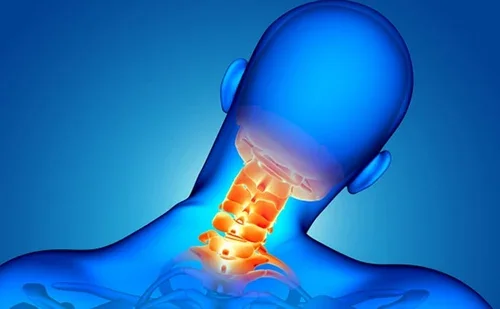
CERVICAL
Neck Region. Injuries here can affect the arms, hands, diaphragm, and trunk. High cervical injuries can result in quadriplegia (loss of function in all four limbs) and may impact breathing.
-
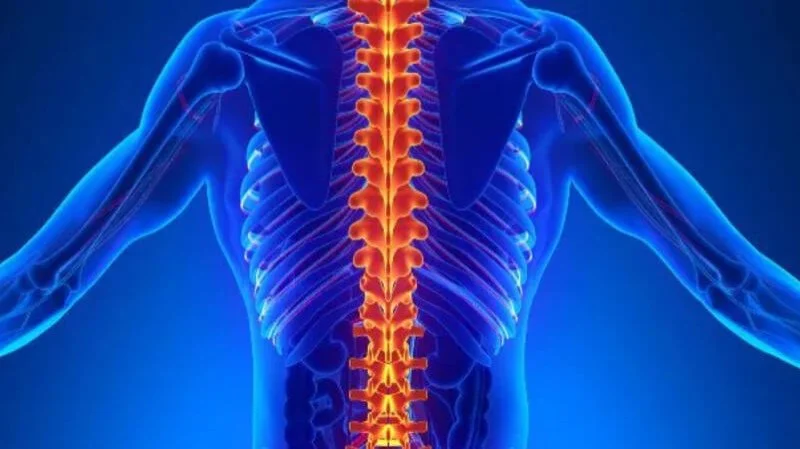
THORACIC
Upper Back. These injuries usually affect the trunk and legs. Arm function is typically preserved, but individuals may experience paraplegia (loss of function in the lower body).
-
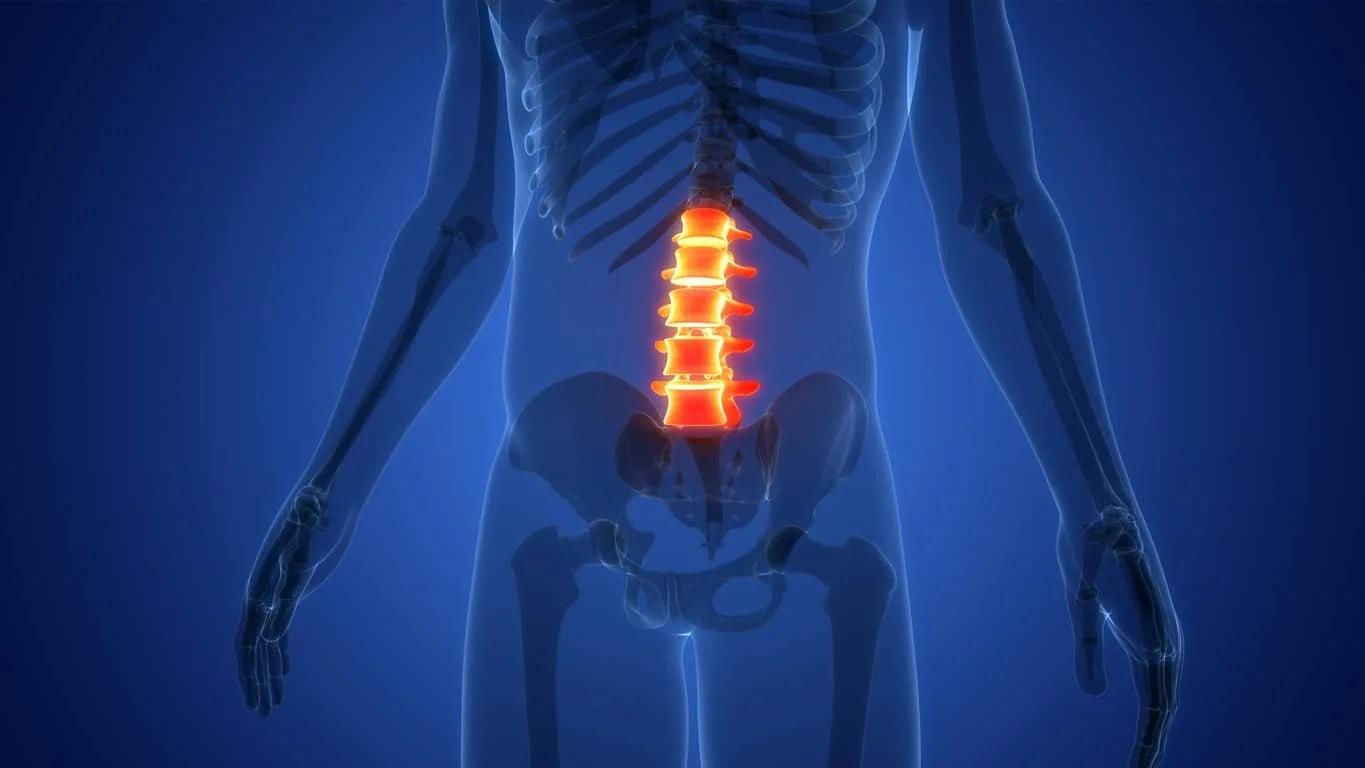
LUMBAR
Lower Back. These injuries primarily affect the hips, legs, and lower trunk. They may result in varying levels of leg weakness or paralysis.
-

SACRAL
Pelvic Area. Injuries here may impact bowel, bladder, and some leg and foot functions.
HOW A SPINAL CORD INJURY (SCI)EFFECTS THE BODY
Musculoskeletal System:
Muscle weakness or paralysis can lead to difficulty moving, maintaining posture, or performing daily activities. Over time, spasticity and joint stiffness may develop.
Sensory System:
Individuals may experience numbness, tingling, or loss of sensation. Some may also develop neuropathic (nerve) pain or hypersensitivity.
Autonomic Nervous System
This system controls involuntary functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature. A SCI can lead to problems such as low blood pressure difficulty sweating, or a potentially dangerous sudden rise in blood pressure.
Bladder and Bowel Function:
Most individuals with SCI have changes in bladder and bowel control. Management may include catheterization, scheduled toileting, or other techniques.
Mental and Emotional Health:
A SCI can be emotionally challenging. It is common to experience anxiety, depression, or grief. Mental health support is a key part of recovery and adjustment.
Respiratory System:
High cervical and some thoracic injuries can affect breathing, coughing, and lung function. Individuals may need respiratory support or exercises to improve breathing efficiency.
Skin and Circulation:
Decreased mobility can lead to pressure injuries (bedsores), especially over bony areas. Poor circulation also increases the risk of swelling and blood clots.
